BLOG 1: Social Determinants of Health
In the realm of healthcare, the focus has traditionally been on diagnosing and treating illnesses. However, in recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of social determinants of health (SDOH)—the non-medical factors that influence health outcomes of the population. For advanced practice nurses, understanding and addressing these determinants is crucial for providing appropriate and effective care.
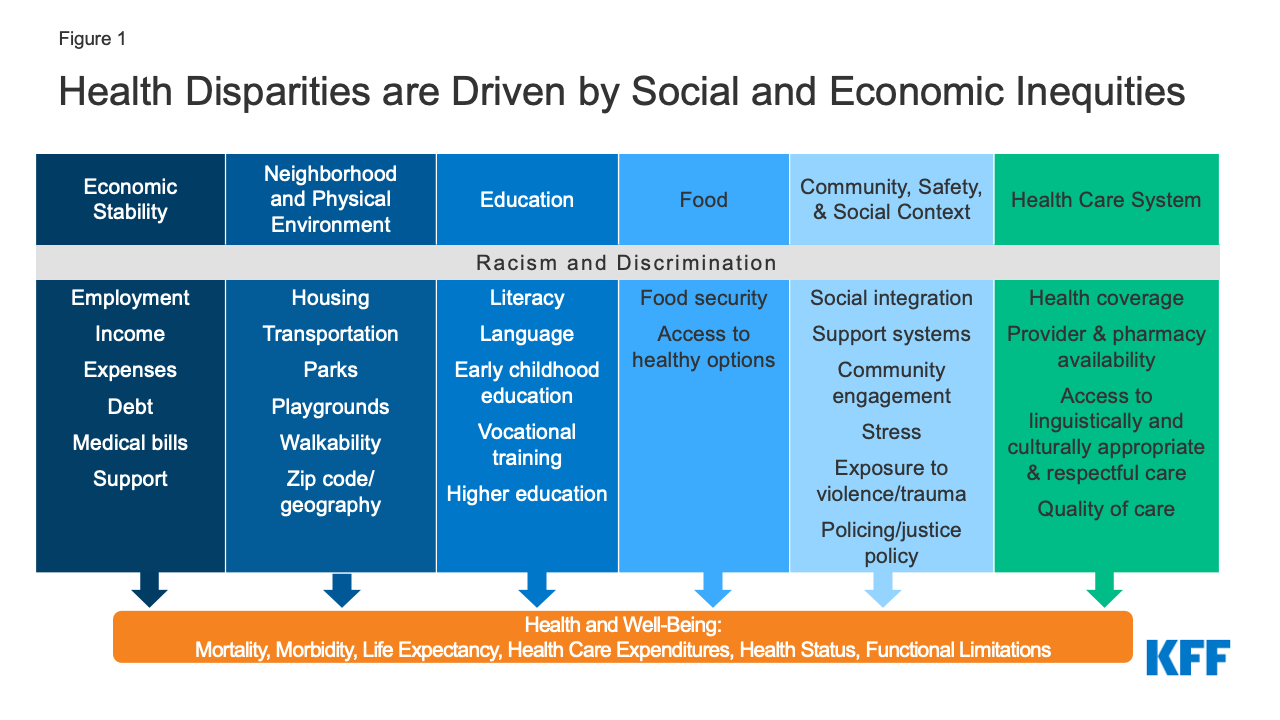
The environment in which people are born, grow, live, work and age are considered to be the social determinants of health, and these factors play a significant role in their overall well being (Bravemen, 2022).
Non-medical factors that affect health outcomes:
- Economic stability: income levels, jobs, and policies can impact access to nutritious food, healthcare, housing, and educational opportunities.
- Education Access and Quality: This influences health literacy, which impacts a person's capabilities to navigate a health system, understands risks and benefits, and make informed decisions about their health.
- Social and Community Context: Social relationships, support network, and social cohesion can affect mental and physical health.
- Health care access and quality: disparities in healthcare access related to geographic location, financial barriers, system challenges can affect health outcomes.
- Environment and neighborhood: Housing, transportation, safety in the neighborhood, affects how individuals live a healthy lifestyle (Bravemen, 2022).
Health: Can be defined as interactions between genes and experiences. Some factors that can affect health are behaviors of an individual, medical care, living and working conditions, communities, economic and social opportunities and resources available for an individual (Youtube, 2017).
Health Disparities: refer to differences in health outcomes and access to healthcare services among different populations. These are usually measurable and can be based factors such as: race and ethnicity, income, geographic location, gender and age, education level (Grumbach e al, 2017).
Health Inequities: unfair and avoidable differences in health outcomes related to health disparities, usually related to systemic issues (Grumbach e al, 2017).

Overcoming health disparities as future providers...
Understanding the population and the community serving is a key factor in being aware of the health disparities that might pose a challenge for delivering care. As future provider, one of the things that we must consider is how we can eliminate health care inequalities. The Institute of Medicine (IOM), reports that disparities in health are associated with worse health outcomes, several factors contribute to disparities including health systems, providers, and patients. IOM also highlights that racial and ethnic disparities are associated with the worse health outcomes, and are more likely to refuse treatments (IOM, n.d.).
Several recommendations made by IOM:
- Increased in awareness of racial and ethnic disparities in general public and stakeholders.
- Increase healthcare provider awareness of racial and ethnic disparities.
- Provide better resources and increase diversity in healthcare professionals.
- Support and conduct more research around ethical issues and barriers to decrease disparity.
- Improve and involve cross-cultural education in training in health (IOM, n.d.).
References
Braveman P (2022). The social determinants of health. Boulton M.L., & Wallace R.B.(Eds.), Maxcy- Rosenau-Last Public Health & Preventive Medicine, 16e. McGraw Hill. https://accessmedicine- mhmedical-com.husson.idm.oclc.org/content.aspx?bookid=3078§ionid=256339268
Grumbach K, & Braveman P, & Adler N, & Bindman A.B. (2016). Vulnerable populations, health disparities, and health equity: an overview. King T.E., & Wheeler M.B.(Eds.), Medical Management of Vulnerable and Underserved Patients: Principles, Practice, and Populations, 2e. McGraw-Hill Education. https://accessmedicine-mhmedical-com.husson.idm.oclc.org/content.aspx?bookid=1768§ionid=119148218
Institute of Medicine findings and recommendations on health ... (n.d.). https://www.ama-assn.org/sites/ama-assn.org/files/corp/media-browser/public/public-health/iom_1.pdf
YouTube. (n.d.). What makes us healthy? Understanding the social determinants of health. . YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8PH4JYfF4Ns
Hi Danijela
ReplyDeleteI enjoyed your post's video analysis of social determinants comparing the life expectancy in Sierra Leone to that of Australia, 50 and 83 years, respectively. By the way, I am from Sierra Leone, and this is the sad reality of my people. Various factors contribute to this disparity, such as individuals living in extreme poverty and struggling to access nutritious food, safe housing, or healthcare services essential for maintaining good health (Braveman & Gottlieb, 2014).
A lot needs to be done to address these issues. The government needs to invest in agriculture, create jobs, etc. Policymakers and healthcare professionals must focus on creating equitable healthcare systems that prioritize preventive care and address the social factors contributing to poor health (Chelak & Chakole, 2023b)
References:
Braveman, P., & Gottlieb, L. (2014). The social determinants of health: It’s time to consider the causes of the causes. Public Health Reports, 129(1_suppl2), 19–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/00333549141291s206
Chelak, K., & Chakole, S. (2023). The Role of Social Determinants of Health in Promoting Health Equality: A Narrative review. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.33425